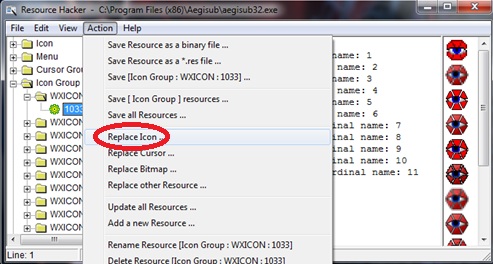
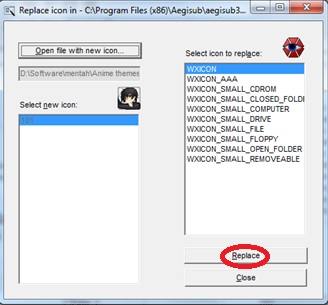
Subject, Verb, Complement & Modifier
SUBJECT
Definition: The subject of a sentence is the noun, pronoun or noun phrase that precedes and governs the main verb. The subject is the part of the sentence that performs an action or which is associated with the action.
For example:
* He is a really nice guy.
* "He" is the subject of the sentence, controlling the verb and the complement.
* My dog attacked the burglar.
* "My dog" is the subject, controlling the verb and the rest of the sentence.
* David plays the piano
* The subject "David" performs the action of "playing the piano".
* The police interviewed all the witnesses.
* The subject the police performs the action of interviewing all the witnesses.
To determine the subject of a sentence, first isolate the verb and then make a question by placing "who?" or "what?" before it. Having identified the Subject, we can see that the remainder of the sentence tells us what the Subject does or did. We refer to this string as the "predicate" of the sentence.
For example:
* Who plays the piano?
=> "David" ( = Subject)
=> "plays the piano" ( = predicate) tells us what David does.
* Who interviewed all the witnesses?
=> "The police" (= Subject)
=> "interviewed all the witnesses" ( = predicate) tell us what the police did.
Subjects can either be "simple", "compound" or "complex"
Simple Subject
Composed of a single pronoun, noun or noun phrase.
Complex Subject
A complex subject consists of a noun phrase and any words, phrases, or clauses that modify it.
For example:
* The man who had followed us inside walked over to the telephone.
=> central noun: man
=> complex subject: the man who had followed us inside
* The superior performance of La Traviata pleased the wealthy audience.
=> central noun: performance
=> complex subject: the superior performance of La Traviata
Compound Subject
A compound subject consists of two or more noun phrases (and their modifiers if any) joined together with a coordinating conjunction.
For example:
* The man and the woman walked over to the telephone.
=> The compound subject here is the whole phrase, "the man and the woman."
* Neither the superior performance of La Traviata nor the excellent wine at intermission pleased the wealthy audience.
=> Again, the whole phrase, "neither the superior performance of La Traviata nor the excellent wine at intermission," is the subject. The phrase answers the question, "What pleased the wealthy audience?"
======================================================
VERBS
Definition: Verbs are a class of words used to show the performance of an action (do, throw, run), existence (be), possession (have), or state (know, love) of a subject. To put it simply a verb shows what something or someone does.
For example:
* Paul rides a bicycle.
* Here, the verb rides certainly denotes an action which Paul performs - the action of riding a bicycle.
* We buy some books to learn English verbs.
* In this example, the action word is "to buy". It tells us that the subject "we", that is the person who performs the action of the verb is "buying some books".
The verb tense shows the time of the action or state. Aspect shows whether the action or state is completed or not. Voice is used to show relationships between the action and the people affected by it. Mood shows the attitude of the speaker about the verb, whether it is a declaration or an order. Verbs can be affected by person and number to show agreement with the subject.
Most statements in speech and writing have a main verb. These verbs are expressed in "tenses" which place everything in a point in time.
Verbs are conjugated (inflected) to reflect how they are used. There are two general areas in which conjugation occurs; for person and for tense.
Conjugation for tense
Conjugation for tense is carried out on all verbs. All conjugations start with the infinitive form of the verb.
The infinitive is simply the to form of the verb For example, to begin.
The present participle form (the -ing form), is formed by adding ing to the bare infinitive. For example, to begin - beginning.
There are two other forms that the verb can take, depending on the tense type and time, the simple past form and the past participle.
The form of the verb or its tense can tell when events take place.
For example, the verb kiss:
Present Simple: kiss/kisses
Past Simple: kissed
Future Simple: will kiss
Present Perfect: has/have kissed
Past Perfect: had kissed
Future Perfect: will have kissed
Present Continuous (Progressive): is/am/are kissing
Past Continuous (Progressive): was kissing
Future Continuous (Progressive): will be kissing
Present Perfect Continuous (Progressive): has/have been kissing
Past Perfect Continuous (Progressive): had been kissing
Future Perfect Continuous (Progressive): will have been kissing
Conjugation for person
Conjugation for person occurs when the verb changes form, depending on whether it is governed by a first, second, or third person subject. This gives three conjugations for any verb depending on who is acting as the subject of the verb. For example: we have I begin, you begin , and he begins. Note that only the third conjunction really shows a difference.
In English, we distinguish between regular and irregular verbs. Regular verbs are those ones which form their past simple and past participle just by adding "-ed" to the base of the verb. The rest are irregular.
Examples:
* Dracula bites his victims on the neck.
* In early October, Giselle will plant twenty tulip bulbs.
* She travels to work by train.
* We walked five miles to a garage.
======================================================
The Grammatical Subject Complement in English
Although nouns and adjectives most frequently function as the subject complement of sentences, five grammatical forms can perform the grammatical function of subject complement in the English language. Both native speakers and ESL students must learn and understand the five forms that can function as the subject complement in order to speak and write English fully and correctly. The five grammatical forms that can function as the subject complement are:
1. Noun phrases
2. Adjective phrases
3. Prepositional phrases
4. Verb phrases
5. Noun clauses
Subject complements are defined as words, phrases, and clauses that follow a copular or linking verb and refer back to modify or describe the subject. Subject complements are grammatical constituents embedded in the predicate of clauses.
Noun Phrases as Subject Complements
The first grammatical form that can perform the grammatical function of subject complement is the noun phrase. Noun phrases are defined as phrases that consist of a noun or pronoun plus any modifiers or complements. For example, the following italicized noun phrases function as subject complements:
* My favorite subject is grammar.
* The professor is an exceptionally intelligent person.
* My sister became a mother last night.
Traditional grammars generally use the term predicate nominative to refer to noun phrases functioning as subject complements.
Adjective Phrases as Subject Complements
The second grammatical form that can perform the grammatical function of subject complement is the adjective phrase. Adjective phrases are defined as phrases that consist of an adjective plus any modifiers or complements.
Sumber
PRONOUNS
A pronoun is used in place of a noun or nouns. Common pronouns include he, her, him, I, it, me, she, them, they, us, and we. Here are some examples:
INSTEAD OF: Luma is a good athlete.
She is a good athlete. (The pronoun she replaces Luma.)
INSTEAD OF: The beans and tomatoes are fresh-picked.
They are fresh-picked. (The pronoun they replaces the beans and tomatoes.)
Often a pronoun takes the place of a particular noun. This noun is known as the antecedent. A pronoun "refers to," or directs your thoughts toward, its antecedent.
Let's call Luma and ask her to join the team. (Her is a pronoun; Luma is its antecedent.)
To find a pronoun's antecedent, ask yourself what that pronoun refers to. What does her refer to in the sentence above—that is, who is the her? The her in the sentence is Luma; therefore, Luma is the antecedent.
Subjective Pronouns
Pronouns
A subjective pronoun acts as the subject of a sentence—it performs the action of the verb. The subjective pronouns are he, I, it, she, they, we, and you.
He spends ages looking out the window.
After lunch, she and I went to the planetarium.
Objective Pronouns
An objective pronoun acts as the object of a sentence—it receives the action of the verb. The objective pronouns are her, him, it, me, them, us, and you.
Cousin Eldred gave me a trombone.
Take a picture of him, not us!
Possessive Pronouns
A possessive pronoun tells you who owns something. The possessive pronouns are hers, his, its, mine, ours, theirs, and yours.
The red basket is mine.
Yours is on the coffee table.
Demonstrative Pronouns
A demonstrative pronoun points out a noun. The demonstrative pronouns are that, these, this, and those.
That is a good idea.
These are hilarious cartoons.
A demonstrative pronoun may look like a demonstrative adjective, but it is used differently in a sentence: it acts as a pronoun, taking the place of a noun.
Interrogative Pronouns
An interrogative pronoun is used in a question. It helps to ask about something. The interrogative pronouns are what, which, who, whom, and compound words ending in "ever," such as whatever, whichever, whoever, and whomever.
What on earth is that?
Who ate the last Fig Newton?
An interrogative pronoun may look like an interrogative adjective, but it is used differently in a sentence: it acts as a pronoun, taking the place of a noun.
Indefinite Pronouns
An indefinite pronoun refers to an indefinite, or general, person or thing. Indefinite pronouns include all, any, both, each, everyone, few, many, neither, none, nothing, several, some, and somebody.
Something smells good.
Many like salsa with their chips.
An indefinite pronoun may look like an indefinite adjective, but it is used differently in a sentence: it acts as a pronoun, taking the place of a noun.
Relative Pronouns
A relative pronoun introduces a clause, or part of a sentence, that describes a noun. The relative pronouns are that, which, who, and whom.
You should bring the book that you love most.
That introduces "you love most," which describes the book.
Hector is a photographer who does great work.
Who introduces "does great work," which describes Hector.
Reflexive Pronouns
A reflexive pronoun refers back to the subject of a sentence. The reflexive pronouns are herself, himself, itself, myself, ourselves, themselves, and yourselves. Each of these words can also act as an intensive pronoun (see below).
I learned a lot about myself at summer camp. (Myself refers back to I.)
They should divide the berries among themselves. (Themselves refers back to they.)
Intensive Pronouns
An intensive pronoun emphasizes its antecedent (the noun that comes before it). The intensive pronouns are herself, himself, itself, myself, ourselves, themselves, and yourselves. Each of these words can also act as a reflective pronoun (see above).
I myself don't like eggs.
The queen herself visited our class.
Sumber
Free Template Blogger
collection template
Hot Deals
BERITA_wongANteng
SEO
theproperty-developer